If you are looking for What your Council Tax pays for – Cambridge City Council you’ve visit to the right place. We have 1 Pics about What your Council Tax pays for – Cambridge City Council like What your Council Tax pays for – Cambridge City Council and also What your Council Tax pays for – Cambridge City Council. Here you go:
Essentially, a tax is a compulsory financial fee or levy imposed upon a taxpayer – be it an individual or a legal entity such as a company – by a governmental organization. The chief purpose of this accumulation is to support various public expenditures, including infrastructure projects such as building bridges and preserving highways to essential services including national defense, law enforcement, public health systems, and education. Without this steady stream of revenue, governments would not be able to provide the services and protections that citizens often rely upon and look for as part of a functioning society, in effect underpinning the stability and order we often take for granted.
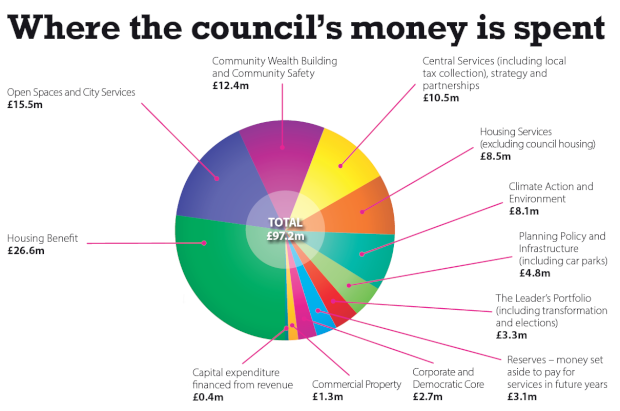
What Your Council Tax Pays For – Cambridge City Council
www.cambridge.gov.uk
The existence of taxation is fundamentally based on the concept of the social contract, an implicit agreement among members of a society to cooperate for social benefits. Citizens contribute a portion of their wealth or income to the state, and in reciprocity, the state provides security, order, infrastructure, and services that benefit the collective whole. This system facilitates the pooling of resources to achieve goals and provide services on a scale that would be impossible for individuals or smaller groups to accomplish independently. It embodies a collective investment in the stability, development, and well-being of the community and the nation, binding individuals together through shared responsibility and benefit.
Nevertheless, the world of taxation is anything but monolithic or simple. Tax systems differ considerably from one country to another, and even within a single nation, many kinds of taxes exist. These can include direct taxes levied on income and wealth, for example personal income tax and corporate profit tax, to indirect taxes imposed on goods and services, for instance Value Added Tax (VAT) or sales tax. Additionally, taxes can be levied on property, inheritance, capital gains, and specific activities or products regarded as harmful or luxurious. The design of these tax systems, including rates, exemptions, and enforcement mechanisms, illustrates a complex interplay of economic goals, political ideologies, and societal values regarding fairness and distribution.
Comprehending the principles and practices of taxation is therefore crucial, not just for economists and policymakers, but for every citizen and business. Taxes influence individual financial decisions, form corporate strategies, fuel economic growth (or hinder it), and support the very structure of our public lives. 1 Debates concerning tax fairness, efficiency, and its impact on economic behavior are constant elements of political discourse worldwide. Investigating this multifaceted subject reveals much about how societies choose to organize themselves, allocate resources, and pursue collective goals, making it an essential topic for anyone seeking to comprehend the mechanics of the modern economy and government.
